-40%
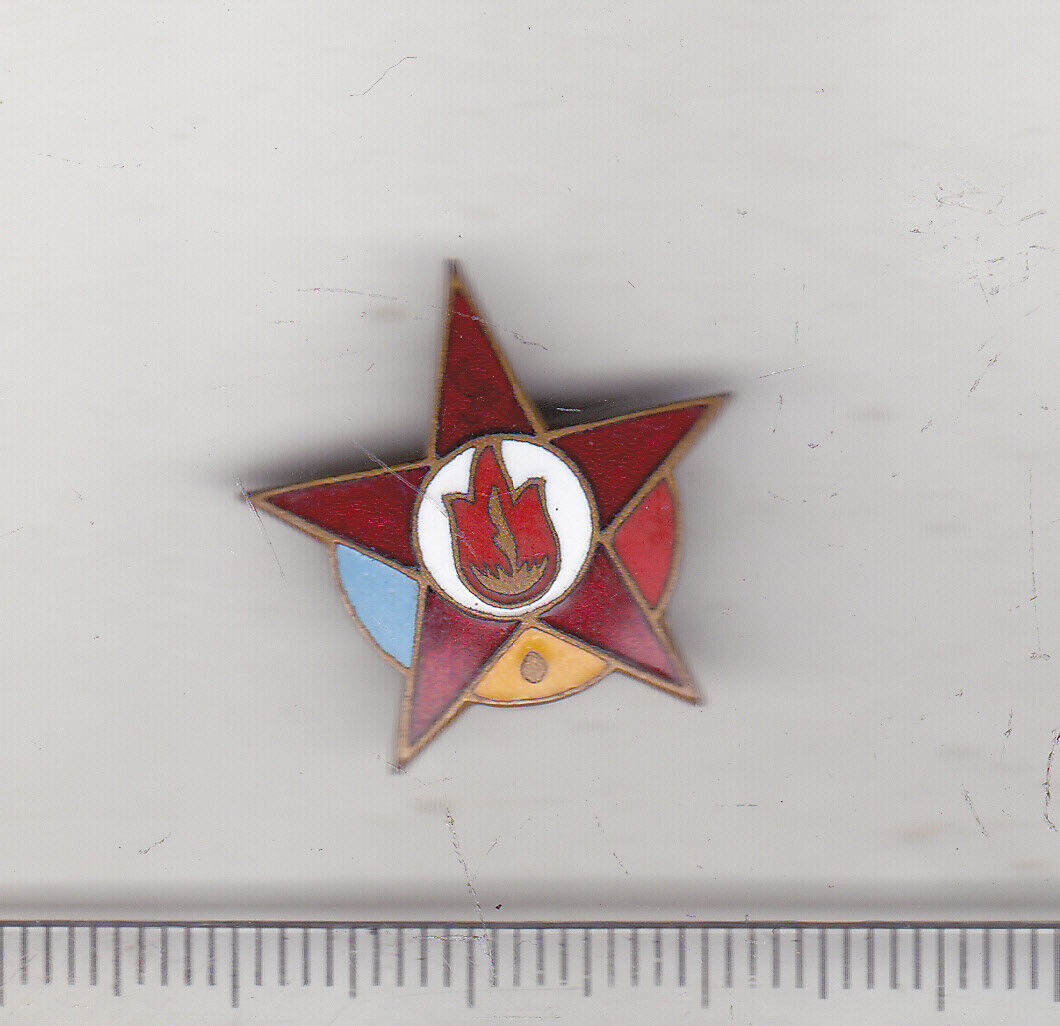
Death & state funeral of Josip Broz Tito LAST SALUTE VOLLEY FIRE ENGRAVED CASING
$ 712.27
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
original genuine collectible documented remnant - original blank casing from the last volley salute fire at Tito's funeral on may 8th 1980.out of 1850 in total, there were only 82 of those with Tito's image and text engraved onto them (the factory that was doing this was Aurometal from Subotica).
all others - 1768 in total - had text on them engraved only.
the first ones printed among those 82 of exclusive ones had a
grammar
printing error in date inclusive of this one. 48 of these 82 exclusive ones were allotted to the Military Museum in Belgrade to be saved as the permanent museum value of the land. two of those were also given to the Military Museum and Political Governance for their symbols collection. the remaining 32 were given to the Museum Director to be given away at his discretion in exceptional cases to the foreign delegations, institutions, and individuals. this one comes from the estate of
Major
General of the Yugoslav Army.
Artillery 76 mm Big and Heavy Brass Shell Case/Casing with all Original Markings on the bottom
M1 - 450; M48 B1; M42 and Tank D 56 TS
height of casing only c. 18 cm
height inclusive of its wooden stand 22.5 cm
radius of casing on top 8 cm
radius of its stand 11.5 cm
The funeral of Josip Broz Tito, President of Yugoslavia, was held on 8 May 1980, four days after his death on 4 May. His funeral drew many world statesmen, both of non-aligned and aligned countries. Based on the number of attending politicians and state delegations, it is the largest state funeral in history. This included four kings, 31 presidents, six princes, 22 prime ministers, and 47 ministers of foreign affairs, from both sides of the Iron Curtain and beyond. In total, 128 countries out of the 154 UN members at the time were represented. Also present were delegates from seven multilateral organizations, six movements and 40 political parties.
Tito had become increasingly ill throughout the course of 1979. On 7 January and again on 11 January 1980, Tito was admitted to the University Medical Centre in Ljubljana, the capital city of SR Slovenia, with circulation problems in his legs. His left leg was amputated soon afterward due to arterial blockages, and he died of gangrene at the Medical Centre Ljubljana on 4 May 1980 at 3:05 pm, three days short of his 88th birthday. The "Plavi voz" (Blue train, official presidential train) brought his body to the Yugoslav capital Belgrade where it lay in state at the Federal Parliament building until the funeral.
By 1979, Tito's health had declined rapidly, mainly due to an arterial embolism in his left leg. In that year, he participated in the Havana Conference of the Non-Aligned Movement and spent New Year's Eve in his residence in Karađorđevo. Throughout the televised event, Tito remained seated while exchanging greetings, causing concern to the watching audience. During this time Vila Srna was built for his use near Morović in the event of his recovery.
On January 3, 1980, Tito was admitted to the Ljubljana University Medical Centre for tests on blood vessels in his leg. Two days later, after the angiography, he was discharged to his residence in Brdo Castle near Kranj, with a recommendation for further intensive treatment. Angiography revealed that Tito's superficial femoral artery and Achilles tendon artery were clogged. The medical council consisted of eight Yugoslav doctors, Michael DeBakey from the United States and Marat Knyazev from the Soviet Union.
Following the advice of DeBakey and Knyazev, the medical team attempted an arterial bypass. The first surgery was done in the night of January 12. At first, the operation appeared to have been a success, but after several hours it became clear that it had not. Due to severe damage to the arteries, which led to the interruption of blood flow and accelerated tissue devitalization of the left leg, Tito's left leg was amputated on January 20, to prevent the spread of gangrene. When Tito was told about the required amputation, he resisted it as long as possible. Finally, after meeting with his sons, Žarko and Mišo, he agreed to the amputation.[citation needed] After the amputation, Tito's health improved and he began rehabilitation. On 28 January, he was transferred from the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery to the Department of Cardiology. In the first days of February his health had improved enough to allow him to perform some of his regular duties.
By the beginning of January 1980, however, it became clear that Tito's life was in grave danger and Yugoslav political leadership secretly began preparations for his funeral.[citation needed] Tito's wish was that he be buried in the House of Flowers on Dedinje hill, that overlooks Belgrade. Moma Marković, a director for Radio Television Belgrade, was summoned by Dragoljub Stavrev, a vice president in the federal government, to devise plans for broadcasting the funeral.[citation needed]
Death
Tito's Blue Train (Plavi voz), train that carried Tito's coffin from Ljubljana to Belgrade.
Tito died in the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery at the University Medical Centre, Ljubljana on May 4, 1980 at 3:05 pm, three days before his 88th birthday. He died on the seventh floor, in a small room on the south-east corner. A commemorative inscription in the main hall later read "Pot do osvoboditve človeka bo še dolga, a bila bi daljša da ni živel Tito" ("The fight for peoples liberation will be a long one, but would have been longer if Tito never lived"). That inscription was later removed. Immediately upon learning of Tito's death, a full extraordinary session of both the Presidency of Yugoslavia and the Presidency of the Central Committee of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia was held in Belgrade starting at 6:00 pm, at which Tito's death was formally declared via a joint statement:
The message from the CIA's FBIS Austria Bureau, regarding the Radio Bucharest announcement of Tito's death, filed on 4 May 1980.
To the working class, all the working people and citizens, and all the nations and nationalities of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia:
Comrade Tito has died.
On the day of May 4th, 1980 at 15:05 in Ljubljana, the great heart of the President of our Socialist Yugoslavia, the President of the Presidency of Yugoslavia, the President of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, Marshal of Yugoslavia, and the Commander-in-chief of the Yugoslav armed forces, Josip Broz Tito, has stopped beating.
Great sorrow and pain is shaking up the working class, nations and nationalities of our country, our every citizen, worker, soldier, war veteran, farmer, intellectual, every creator, pioneer and youth, and every girl and mother.
For all his entire life, Tito was a fighter for interests and goals of working class, for the most humane ideals, and desires of our nations and nationalities. Tito is our dearest friend. Seven decades he was burning up in a workers movement. For six decades, he strengthened Yugoslav Communists. For more than four decades, he was the leader of our Party. He was a heroic leader in World War II and in the Socialist revolution. For three and a half decades he led our Socialist country, and he moved our country and our fight for fairer human society into the world history, proving that way to be our most important historic world personality.
During the most fateful times of our survival and development, Tito was bold and worthy of carrying the proletarian flag of our revolution, persistently and consistently linked to the fate of nations and man. He fought all throughout his life and work, lived the revolutionary humanism and fervor with enthusiasm and love for the country.
Tito was not only a visionary, critic and translator of the world. He reviewed the objective conditions and patterns of social movements, into the great ideals and thoughts into action with the million masses of the people that were with him at the helm, and made epochal progressive social transformations.
Thus, forever shall his revolutionary work remembered for all time in the history of the people and nationalities of Yugoslavia and in the history of the independence of all of humankind.
—Signed, The Central Committee of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia and the Presidency of Yugoslavia, Belgrade, May 4, 1980.
—
After the declaration was read, Stevan Doronjski (President of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia) said, "Eternal glory be to the memory of our great leader and father of the revolution, President of Yugoslavia and General Secretary and President of the League, our comrade Josip Broz Tito."
At the same meeting, in accordance with the 1974 Yugoslav Constitution, as amended, it was decided that Lazar Koliševski, Vice President of the Presidency of Yugoslavia, would temporarily take the office of the President of the Presidency of Yugoslavia, and that Cvijetin Mijatović, former member of the Presidency of SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, would take Koliševski's place as state vice president. In accordance with the LCY Statute as amended, former chairman of Presidency of Central Committee of League of Communists of Yugoslavia Stevan Doronjski assumed the post of President of the Presidency of the Central Committee of League of Communists of Yugoslavia. Immediately afterwards the Federal Executive Council (government of Yugoslavia) decided to formally announce a week of national mourning across the country.[citation needed]
Grief in the nation
Front pages of Yugoslav magazines dedicated to Tito's death and funeral.
Citizen's usual activities were interrupted when TV screens went black for 30 seconds. After that, Miodrag Zdravković, newsreader of Radio Television Belgrade, read the following statement live with chroma key:
Comrade Tito has died. That was announced tonight by the Central Committee of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia and the Presidency of Yugoslavia to the working class, all the working people and citizens and all the nations and nationalities of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.[8]
The same announcement was read out on the TV stations of each constituent republic in their respective languages.
On Sunday afternoons, Yugoslav Television often broadcast association football games of the Yugoslav First League. That day, there was a league match in Split between NK Hajduk Split and FK Crvena Zvezda.[8] When the match was in its 41st minute, three men entered the Poljud Stadium pitch, signaling the referee to stop the match. Ante Skataretiko, the president of Hajduk, took the microphone and announced Tito's death. What followed were sudden scenes of mass crying with some players such as Zlatko Vujović collapsing down to the ground and weeping. Players of both teams and referees aligned to stand in a moment of silence. Once the stadium announcer said "May he rest in peace", the entire stadium of 50,000 football fans spontaneously started to sing "Comrade Tito we swear to you, from your path we will never depart" (sr).[8][9] The match was halted, and replayed later in the month.[citation needed]
Grief for the statesman's death was largely based on his place in the Yugoslav political scene. He had lead the fight against Nazi German occupation in the Second World War and helped to create the second Yugoslavia. In addition he had again stood for Yugoslav independence by going against Joseph Stalin in 1948, securing for his country a self-determined path, unlike some Eastern Bloc states that were more dependent on Moscow.[10]
Dignitaries
Nations that sent state delegations.
Nations that did not send state delegations, but organizations from those nations did.
Nations that did not send state delegations
State funeral of Josip Broz Tito
The "Plavi voz" (Blue train, official presidential train) brought an empty coffin to the capital Belgrade, due to the bad condition of his deceased body. Tito was actually transferred to Belgrade by a military helicopter.
Tito's funeral drew many statesmen to Belgrade. Two notably absent statesmen were Jimmy Carter and Fidel Castro. His death came just as the 1979 Soviet invasion of Afghanistan had ended the American-Soviet détente. Yugoslavia, though a communist state, was non-aligned during the Cold War due to the Tito-Stalin split in 1948.
After learning that Chinese Premier Hua Guofeng would lead the Chinese delegation, the ailing Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev decided to lead his nation's delegation. In order to avoid meeting Brezhnev whilst in the middle of his campaign for the 1980 United States presidential election, Carter opted to send his mother Lilian Carter and Vice President Walter Mondale as heads of the US delegation. After realizing that leaders of all Warsaw Pact nations would attend the funeral, Carter's decision was criticized by presidential candidate George H. W. Bush as a sign that the United States "inferentially slams Yugoslavs at time that country has pulled away from Soviet Union".[11] Carter visited Yugoslavia later in June 1980 and made a visit to Tito's grave.[12][13]
Helmut Schmidt, chancellor of West Germany, was highly active at the funeral, meeting with Brezhnev, East Germany's Erich Honecker, and Poland's Edward Gierek. British prime minister Margaret Thatcher sought to rally world leaders in order to harshly condemn the Soviet invasion.[citation needed] While she was in Belgrade, she held talks with Kenneth Kaunda, Schmidt, Francesco Cossiga, and Nicolae Ceaușescu. Brezhnev met with Kim Il-sung and Honecker. James Callaghan, leader of the British Labour Party, explained his presence in Belgrade as an attempt to warm relations between his party and Yugoslav communists, which was severed more than a decade ago after dissident Milovan Đilas was welcomed by Jennie Lee, Minister for the Arts under Harold Wilson. Mondale avoided the Soviets, ignoring Brezhnev while passing close to him. Soviet and Chinese delegations also avoided each other.[citation needed]
The pomp and scale of the funeral had been widely documented and the event was a source of pride for the country for years to come. On the fifteenth anniversary of his death in 1995, the Croatian newspaper Arkzin noted that "turbulent times still do not allow for a truly historical assessment of his stature and achievements, but the appraisal which the world showed those days in May 1980, confirms that small nations and small states may produce world giants."[14]
Tito was interred twice on May 8. The first interment was for cameras and dignitaries. The grave was shallow with only a 200 kg (440 lb) replica of the sarcophagus. The second interment was held privately during the night.[citation needed] His coffin was removed, and the shallow grave was deepened. The coffin was enclosed with a copper mask and interred again into a much deeper grave which was sealed with cement and topped with a 9-ton sarcophagus.[citation needed] Communist officials were afraid that someone might steal the corpse, as had happened to Charlie Chaplin. However, the 9 ton sarcophagus had to be put in place with a crane, which would make the funeral unattractive.[citation needed]
In stark contrast to the pageantry of the funeral, Tito's tomb was constructed of marble with a simple inscription that states JOSIP BROZ - TITO 1892–1980. It did not incorporate a red star or any emblem linked to communism. Historians[who?] stated that the burial location, which was the garden of the place he lived during the postwar years more popularly known as the House of Flowers, was selected according to Tito's wishes.[15] The House of Flowers, together with the Museum of Yugoslavia, has since become a tourist destination and landmark of Belgrade visited by millions of people.[citation needed]
State delegations
Source: Mirosavljev, Radoslav (1981). Titova poslednja bitka (Tito's Last Battle) (in Serbo-Croatian). Beograd: Narodna knjiga. pp. 262–264.
Heads of state
State delegations of the below countries were lead by their heads of state:
Algeria: Chadli Bendjedid (President), Mohammed Seddik Benyahia (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Austria: Rudolf Kirchschläger (President), Bruno Kreisky (Federal Chancellor), Willibald Pahr (Foreign Minister)
Bangladesh: Ziaur Rahman (President), Muhammad Shamsul Haque (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Belgium: King Baudouin I, Wilfried Martens (Prime Minister), Henri Simonet (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Bulgaria: Todor Zhivkov (Chairman of the State Council)
Canada: Edward Schreyer (Governor General)
Czechoslovakia: Gustáv Husák (President), Miloš Jakeš (First Secretary of the Communist Party), Bohuslav Chňoupek (Ministers of Foreign Affairs)
Ethiopia: Mengistu Haile Mariam (Chairman of the Derg)
Finland: Urho Kekkonen (President), Paavo Väyrynen (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Greece: Konstantinos Tsatsos (President)
Guinea: Ahmed Sékou Touré (President), Moussa Diakité (Foreign minister)
Guinea-Bissau: Luís Cabral (President)
Hungary: János Kádár (General Secretary of the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party)
Iraq: Saddam Hussein (President), Sa'dun Hammadi (Foreign Minister)
Ireland: Patrick Hillery (President), George Colley (Tánaiste)
Italy: Sandro Pertini (President), Francesco Cossiga (Prime Minister)
Jordan: King Hussein, Abdelhamid Sharaf (Prime Minister)
Cyprus: Spyros Kyprianou (President), Nicos A. Rolandis (Foreign Minister)
North Korea: Kim Il-sung (President), Ho Dam (Foreign Minister)
Cambodia Democratic Kampuchea: Khieu Samphan (President of the State Presidium) (Note: This delegation represented the UN recognized government of Cambodia (Coalition Government of Democratic Kampuchea), although in 1980 Cambodia was de facto ruled as the People's Republic of Kampuchea.[16]
Luxembourg: Jean (Grand Duke), Gaston Thorn (Deputy Prime Minister)
Mali: Moussa Traoré (President), Alain Blondel Bey (Foreign Minister)
Malta: Anton Buttigieg (President)
East Germany: Erich Honecker (General Secretary of the Central Committee and the Chairman of the State Council), Oskar Fischer (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
West Germany: Karl Carstens (President), Helmut Schmidt (Chancellor), Hans-Dietrich Genscher (Foreign Minister)
Norway: King Olav V, Odvar Nordli (Prime Minister)
Pakistan: Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq (President), Riaz Piracha (Foreign Secretary)
Panama: Aristides Royo (President), Carlos Osores (Foreign Minister)
Poland: Edward Gierek (First Secretary of the Polish United Workers' Party), Wojciech Jaruzelski (Minister of National Defence)
Portugal: António Ramalho Eanes (President), Francisco de Sá Carneiro (Prime Minister)
Romania: Nicolae Ceaușescu (President), Ilie Verdeț (Prime Minister), Ștefan Andrei (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
San Marino: Pietro Chiaruzzi and Primo Marani (Captains Regent)
Soviet Union: Leonid Brezhnev (General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party, Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet), Andrei Gromyko (Ministry of Foreign Affairs)
Sweden: King Carl XVI Gustaf, Ola Ullsten (Minister for Foreign Affairs)
Syria: Hafez al-Assad (President), Abdul Halim Khaddam (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Tanzania: Julius Nyerere (President), Benjamin Mkapa (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Togo: Gnassingbé Eyadéma (President)
Zambia: Kenneth Kaunda (President)
Heads of government or vice-heads of state
State delegations of those countries were headed by their heads of government or vice-heads of state:
Afghanistan: Sultan Ali Keshtmand (First Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers), Shah Mohamad Dost (Foreign Minister)
Burma: Maung Maung Kha (Prime Minister)
Cape Verde: Pedro Pires (Prime Minister)
China: Hua Guofeng (Premier), Ji Pengfei (Secretary General of the State Council)
Colombia: Gustavo Balcázar Monzón (Vice President)
Egypt: Hosni Mubarak (Vice President)
France: Raymond Barre (Prime Minister), Jean François-Poncet (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Ghana: Joseph W.S. deGraft-Johnson (Vice-President), Isaac Chinebuah (Minister for Foreign Affairs)
Guyana: Ptolemy Reid (Deputy Prime Minister)
India: Indira Gandhi (Prime Minister)
Indonesia: Adam Malik (Vice President)
Japan: Masayoshi Ōhira (Prime Minister)
Madagascar: Désiré Rakotoarijaona (Vice President of the Supreme Revolutionary Council)
Mongolia: Jambyn Batmönkh (Prime Minister)
Netherlands: Prince Claus (Prince consort), Prince Bernhard (former Prince consort), Dries van Agt (Prime Minister), Chris van der Klaauw (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
North Yemen: Qadi Abdel (Vice President)
Peru: Pedro Richter Prada (Prime Minister)
Spain: Adolfo Suárez (Prime Minister), Marcelino Oreja, 1st Marquis of Oreja (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Turkey: Süleyman Demirel (Prime Minister), Hayrettin Erkmen (Foreign Minister)
United Kingdom: Prince Philip (Prince consort), Margaret Thatcher (Prime Minister), Lord Carrington (Foreign Secretary), Fitzroy Maclean (wartime British liaison to Yugoslav partisan troops, personal friend of Tito).
United States: Walter Mondale (Vice President), Lillian Gordy Carter (mother of President Jimmy Carter) and W. Averell Harriman (former Governor of New York).
Zimbabwe: Robert Mugabe (Prime Minister)
Deputies or foreign ministers
Delegations of those countries were headed by their deputy heads of state, deputy heads of government or their foreign ministers:
Australia: Andrew Peacock (Minister for Foreign Affairs)
Bolivia: Gaston Aroas Levi (Chancellor)
Brazil: Oto Agripino Maia (Foreign Minister)
Cameroon: Jean Keucha (Foreign Minister)
Cuba: Isidoro Malmierca Peoli (Foreign Minister)
Denmark: Henrik (Prince Consort), Kjeld Olesen (Foreign Minister)
Iran: Sadegh Ghotbzadeh (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Mauritius: Harold Edward Water (Foreign Minister)
Mexico: Enrique Olivares Santana (Deputy Prime Minister)
Nigeria: Ishaya Audu (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Nicaragua: Miguel d'Escoto Brockmann (Foreign Minister)
New Zealand: Brian Talboys (Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Seychelles: Jacques Hodoul (Minister for Foreign Affairs)
Sri Lanka: Abdul Cader Shahul Hameed (Minister of External Affairs)
Switzerland: Pierre Aubert (Foreign Minister)
Thailand: Thanat Khoman (Deputy Prime Minister)
Uganda: Otema Allimadi (Foreign Minister)
Venezuela: José Zambrano Velasco (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Vietnam: Huỳnh Tấn Phát (Deputy Prime Minister)
Other state delegations
State delegations of those countries were headed by government ministers, ambassadors or royal house members:
Andorra:[who?]
Angola: Ambrósio Lukoki (Minister of Education and Member of the Politburo of MPLA)
Argentina: Alberto Rodríguez Varela (Minister of Justice)
Bahamas:[who?]
Benin: Tonakpon Capo-Chichi (Minister of Culture) and Agbahe Gregoire (Minister of Tourism and Crafts)
Botswana: A. V. Kgarebe (High Commissioner to the United Kingdom)
Brazil: Jose Ferraz de Rosa (Army General, State Minister, and General Chief of Staff)
Burundi: Reni Nkonkengurute (Member of the Politburo and Presidium of the Central Committee of the Union for National Progress, Minister for Presidency affairs)
Central African Republic: General Mbale (Minister of Internal Affairs)
Ecuador: Mario Aleman (Sub-secretary of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs)
Equatorial Guinea: Abaga Julian Esono (Ambassador to France)
Philippines: Leon ma Guerrero (Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Gabon: Jean Robert Fungu (Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Iceland: Ingvi Sigurður Ingvarsson (Ambassador to Sweden, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Jamaica: K. G. Hill (Ambassador to Geneva, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Kenya: Okvanyo (Trade minister)
Republic of the Congo People's Republic of the Congo:[who?]
Costa Rica: Fernando Aldman (Minister of economy)
Kuwait: Sheikh Abdullah al Jaber (Special emissary of Prime minister Emir Jaber al Ahmad)
Lebanon: Ali el Halil (Minister of finance)
Liberia: Robert Kvele Kennedy (Ambassador to Rome, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Libya: Abu-Bakr Yunis Jabr (Minister of Defense, General of Army)
Liechtenstein: Walter Oehry, Mario Ledebur
Maldives: Ahmed Zaki (Permanent Representatives of the Maldives to the UN)
Malaysia: Abdul Taib Mahmud (Minister of Defence)
Morocco: Dej Ould Sidi (President of Parilament), Mohammed Doniri
Mauritania: Mohamme Ulg el-Hussein (Minister)
Monaco:[who?]
Mozambique:[who?]
Nepal: Prince Gyanendra of Nepal and K. B. Shahi (Minister of Foreign Affairs)
Niger: Mahamane Karmou (Ambassador to USSR, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Ivory Coast: K. Nalobamba (State Minister), Tousagnon Benoit
Oman: Fahad bin Mahmoud Al-Said (Deputy Prime Minister)
Rwanda: Jules Kanadra (Ambassador to Moscow, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
São Tomé and Príncipe:[who?]
Senegal:[who?]
Sierra Leone: Philip Faboe (Secretary of State)
Singapore: David Marshall (Ambassador to France)
Somalia: Ismail Ali Abokor (President of the People's Assembly, and Member of the Politburo of the Central Committee of the Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party)
South Yemen: M. S. Muti (Member of the Politburo and Secretary of the Central Committee of the Yemeni Socialist Party)
Sudan: Sherif Ghasim (Member of the Politburo of the Sudanese Socialist Union)
Trinidad and Tobago: James O'Neil (Ambassador to Brussels, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Tunisia: Sadok Mokaddem (President of the Assembly, and Member of the Politburo of the Socialist Destourian Party) and Habib Bourguiba, Jr.
Upper Volta: Tiemoko Marc Garango (Ambassador to West Germany, non-resident Ambassador to Yugoslavia)
Uruguay: Walter Ravenna (Minister of National Defense)
Vatican City: Achille Silvestrini (Secretary of the Council for Public Affairs of the Church)
Zaire: Nzondomyo a' Dokpe Lingo (President of the National Assembly)
Delegations of parties and organizations
International organizations
Arab League: Chedli Klibi (Secretary-General)
European Union European Parliament: Simone Veil (President)
European Union Council of Europe: Franz Karasek (Secretary General)
European Union European Commission: Wilhelm Haferkamp (Vice-President)
OECD: Emiel van Lennep (Secretary-General)
United Nations: Kurt Waldheim (Secretary-General)
UNESCO: Amadou-Mahtar M'Bow (Director-General)
Liberation movements
Kurdistan Peoples Liberation Army: Abdullah Öcalan (Leader)
Palestine Liberation Organization: Yasser Arafat (Chairman)
Polisario Front: Mohamed Abdelaziz (Chairman of the Revolutionary Council)
Provisional Irish Republican Army: Billy McKee (Leader)
SWAPO: David Meroro (President of the People's Assembly)
Umkhonto we Sizwe: Chris Hani (Chief of staff)
Political parties
Algeria National Liberation Front: Abdelaziz Bouteflika (president)
Austria Communist Party of Austria: Franz Muhri (president)
Belgium Communist Party of Belgium: Louis Van Geyt (president)
Cyprus Progressive Party of Working People: Ezekias Papaioannou (Secretary General)
Denmark Communist Party of Denmark: Jørgen Jensen (president)
Denmark Socialist People's Party: Gert Petersen (president)
France Communist Party of France: Georges Marchais (Secretary general)
France Socialist Party: François Mitterrand (First secretary)
France Unified Socialist Party: Huguette Bouchardeau (National secretary)
Greece Communist Party of Greece (Interior): Babis Drakopoulos (Secretary General)
Greece Communist Party of Greece: Charilaos Florakis (Secretary General)
Greece PASOK: Andreas Papandreou (Secretary General)
Netherlands Communist Party of the Netherlands: Henk Hustra (president)
Netherlands Labour Party: Joop den Uyl (Parliamentary group leader)
Republic of Ireland Communist Party of Ireland: Andy Barr (president)
Republic of Ireland Sinn Féin: Ruairí Ó Brádaigh (Chairman)
Italy Communist Party of Italy: Enrico Berlinguer (Secretary General)
Italy Italian Socialist Party: Bettino Craxi (Secretary General)
Lebanon Lebanese Communist Party: Nicolas Shawi (Secretary General)
Lebanon Progressive Socialist Party: Walid Jumblatt (President)
Malta Labour Party: Karmenu Mifsud Bonnici (Deputy leader)
Morocco Socialist Union of Popular Forces: Abderahime Buabid (Secretary General)
Morocco Party of Progress and Socialism: Ali Yata (Secretary General)
Mauritius Communist Party of Mauritius: President
West Germany Social Democratic Party of Germany: Willy Brandt (President and President of the Socialist International)
Nigeria National Party of Nigeria: Augustus Akinloye (President)
Portugal Portuguese Communist Party: Álvaro Cunhal (Secretary General)
Portugal Socialist Party: Mário Soares (Secretary General)
San Marino Sammarinese Communist Party: Umberto Barulli (Secretary General)
South Africa African National Congress: Oliver Tambo (President)
South Africa South African Communist Party: Moses Mabhida (Secretary General)
Spain Communist Party of Spain: Santiago Carrillo (Secretary General)
Spain Spanish Socialist Workers' Party: Felipe González (Secretary General)
Sri Lanka Sri Lanka Freedom Party: Sirimavo Bandaranaike (President)
Switzerland Swiss Party of Labour: Jean Vincent (honorary President)
Sweden Swedish Left Party – Communists: Lars Werner (President)
Turkey Republican People's Party: Bülent Ecevit (President)
Turkey Communist Party of Turkey: İsmail Bilen (General Secretary)
United Kingdom Communist Party of Britain: Gordon McLennan (Secretary General)
United Kingdom Labour Party: James Callaghan (Leader)